Definition of Subdural hematoma - Subdural bleeding
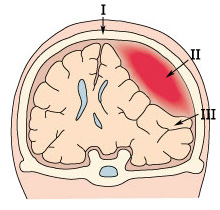
I. The skull
II. Bleeding
III. Compression of the brain
The bleeding continues and gradually pushes
the brain towards the opposite side of the skull.
The pressure around the brain increases which
results in progressive symptoms as the compressed
brain tissue can no longer function normally.
Bleeding under the hard meninges, or membrane, subdural bleeding, is caused by a rupture of one of the blood vessels between the hard meninges and the brain.
This condition is the result of a blow to the head. In young, healthy people this would have to be a strong blow to the head, but in the elderly, or people who for some time have had a high consumption of alcohol, also an insignificant blow might result in a subdural haemorrhage. The reason is a slight shrinkage of the brain resulting in expanded and fragile blood vessels.
When the blood vessel is ruptured it will bleed for some time. Slowly blood will accumulate in the space between the hard outer brain membrane and the inner soft membrane (and thus the brain) and this will result in compression of the brain. The process can be slow and it might be weeks before clear symptoms develop.
Symptoms of subdural bleeding
The symptoms usually don't appear before several days or weeks after the blow and perhaps the patient cannot even remember having hit the head. The symptoms are:
- Confusion, drowsiness or lethargy
- Paralysis in the arms or legs
- Sensory disturbance
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness, difficulty in keeping balance or coordination problems
- Persistent headache and anxiety
If left untreated the symptoms will worsen slowly and possibly ending with unconsciousness and irreversible brain damage or death.
Precautions and treatment of subdural bleeding
If you experience the mentioned symptoms you should seek medical attention immediately. It should be noted that some of the symptoms such as headache, Dizziness, etc are non-specific and seen in a variety of common and harmless conditions. If, as relatives, you note such symptoms in someone at risk (the elderly, alcoholics) action is needed to take the person to the doctor. It is important to mention to the doctor that there might have been a blow to the head.
The doctor will perform a CT scan of the brain (see: image of the brain), where a subdural hemorrhage will show. If the bleeding is significant a small burr hole in the skull will be made which will reduce the pressure and thus the symptoms almost immediately. If the bleeding is small the patient will be monitored closely until the blood has dissolved or been re-absorbed.
Outlook
Rehabilitation will in many cases show good results if the patient has suffered damage to the brain in the process.
Przeczytaj ten artykuł w języku polskim |