Definition and causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition where there is pain and impaired tactile sense of skin, some fingers, the palm of the hand and the wrist due to pressure on a nerve.
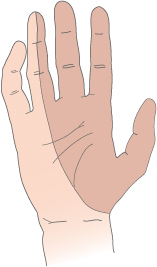
The median nerve connects with the
thumb, the index, long and part of the ring finger which is where the symptoms
will occur.
The wrist is formed by two rows of small bones called the wrist bones or carpal bones. These form the basic structure of the hand and connecti the two forearm bones and the hand. The wrist bones are positioned in a way that, together with ligaments, they form a narrow channel through which among other things one of the nerves, the Median nerve, extends to the hand and fingers. This channel is called the Carpal tunnel.
If the space in Carpal tunnel gets too tight, for example due to swelling, there will be pressure on the nerve, causing pain and sensory disturbances in the fingers (especially from finger 1 to 3), in the palm of the hand and the wrist. Sometimes the condition affects both hands.
The disease can affect several groups. The most common are:
- Middle-aged and elderly women.
- Pregnant women, due to swelling in the Carpal Tunnel.
- People with a rheumatic disorder, or who have had a fracture of the wrist which has resulted in narrowing of the above mentioned channel.
- Carpal Tunnel syndrome might arise from unknown causes.
- People with repetitive working movements of the wrist.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
The most common symptoms are:
- Tingling/stinging sensation in the thumb, index finger, middle finger and on the inside of the ring finger (all these are related to this specific nerve) and in the wrist region.
- Aggravation of the condition at night
- At times, impaired function of certain muscles in the hand and pain all day.
Precautions and diagnosis
If, such symptoms persist for a longer period the doctor should be consult. By clinical examination, the doctor may either make a diagnosis or refer to a specialist who can carry out further investigations.
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
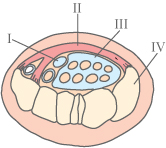
I. Median nerve. II. Tight ligament.
III. Other nerves. IV. Carpal bones.
Cross section of the wrist. - When the
tissue in the carpal tunnel swells the
median nerve is squeezed between
the tight ligament and the carpal bones.
This results in numbness, tingling and
other sensory disturbance.
If Carpal Tunnel syndrome has occurred during pregnancy or other illness, the condition will often disappear when the pregnancy is over, or when the underlying disease is treated.
When there is inflammation the treatment is typically anti inflammatory drugs such as Voltaren, Ibuprufen or similar products and even also injections with corticosteroid drugs . Besides, the wrist might be supported by a splint.
If the condition persists the next step might be surgery to create more space in the Carpal tunnel. This is done by making an incision in the ligament that runs over Carpal tunnel. Depending on how long there has been compression on the nerve, the symptoms will gradually disappear and the result is usually good.
Outlook and complications
The disease has a good prognosis if treated, and complications are relatively modest.
Without treatment the condition might accelerate and result in complete numbness in the hand and reduced force when attempting to grab and hold objects. Similarly, the thumb muscles might slowly weaken if not kept active by the nerve.
Przeczytaj ten artykuł w języku polskim |